Definition of Medical Device and Medical Equipment
a) Medical Device: According to the Medical Devices Regulations 2002 (SI 2002 No 618, as amended) (UK MDR 2002), a medical device is described as any instrument, apparatus, appliance, software, material or other article, whether used alone or in combination, together with any accessories, including the software intended by its manufacturer to be used specifically for diagnosis or therapeutic purposes or both and necessary for its proper application, which is intended by the manufacturer to be used for human beings for the purpose of:
- diagnosis, prevention, monitoring, treatment or alleviation of disease
- diagnosis, monitoring, treatment, alleviation of or compensation for an injury or handicap
- investigation, replacement or modification of the anatomy or of a physiological process, or
- control of conception
A medical device does not achieve its main intended action by pharmacological, immunological or metabolic means although it can be assisted by these. A medical device includes devices intended to administer a medicinal product or which incorporate as an integral part a substance which, if used separately, would be a medicinal product and which is liable to act upon the body with action ancillary to that of the device.
Software as a Medical Device: The term “Software as a Medical Device” (SaMD) is defined as software intended to be used for one or more medical purposes that perform these purposes without being part of a hardware medical device.
b) Medical Equipment: Medical equipment is defined by the World Health Organisation (WHO) as Medical devices requiring calibration, maintenance, repair, user training, and decommissioning – activities usually managed by clinical engineers.
Medical equipment is a subset of medical devices and is also defined as all devices that are connected to the patient as part of their treatment and care in hospitals and health centres, and devices used for diagnostic purposes.
Why it is needed
Medical equipment according to the World Health Organisation (WHO) is used for the specific purposes of diagnosis and treatment of disease or rehabilitation following disease or injury; it can be used either alone or in combination with any accessory, consumable, or other piece of medical equipment. Medical equipment excludes implantable, disposable or single-use medical devices.
Medical equipment is designed to aid in the diagnosis, monitoring or treatment of medical conditions.
Types
There are several basic types:
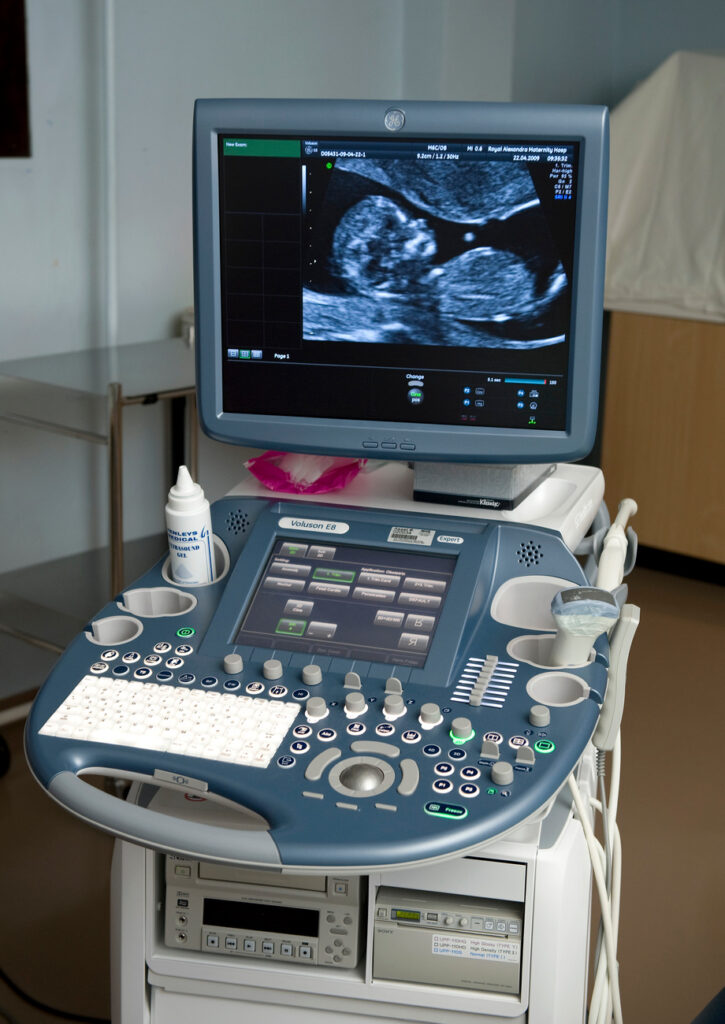
- Diagnostic equipment includes medical imaging machines, used to aid in diagnosis. Examples are ultrasound and MRI machines, PET and CT scanners, and x-ray machines.
- Treatment equipment includes infusion pumps, medical lasers and LASIK surgical machines.
- Life support equipment is used to maintain a patient’s bodily function. This includes medical ventilators, incubators, anaesthetic machines, heart-lung machines, ECMO, and dialysis machines.
- Medical monitors allow medical staff to measure a patient’s medical state. Monitors may measure patient vital signs and other parameters including ECG, EEG, and blood pressure.
- Medical laboratory equipment automates or helps analyze blood, urine, genes, and dissolved gases in the blood.
- Diagnostic medical equipment may also be used in the home for certain purposes, e.g. for the control of diabetes mellitus
- Therapeutic: physical therapy machines like continuous passive range of motion (CPM) machines
The identification of medical devices has been recently improved by the introduction of Unique Device Identification (UDI) and standardised naming using the Global Medical Device Nomenclature (GMDN) which have been endorsed by the International Medical Device Regulatory Forum (IMDRF).
